3D Printing Optimizes the Rimac Nevera's Powertrain
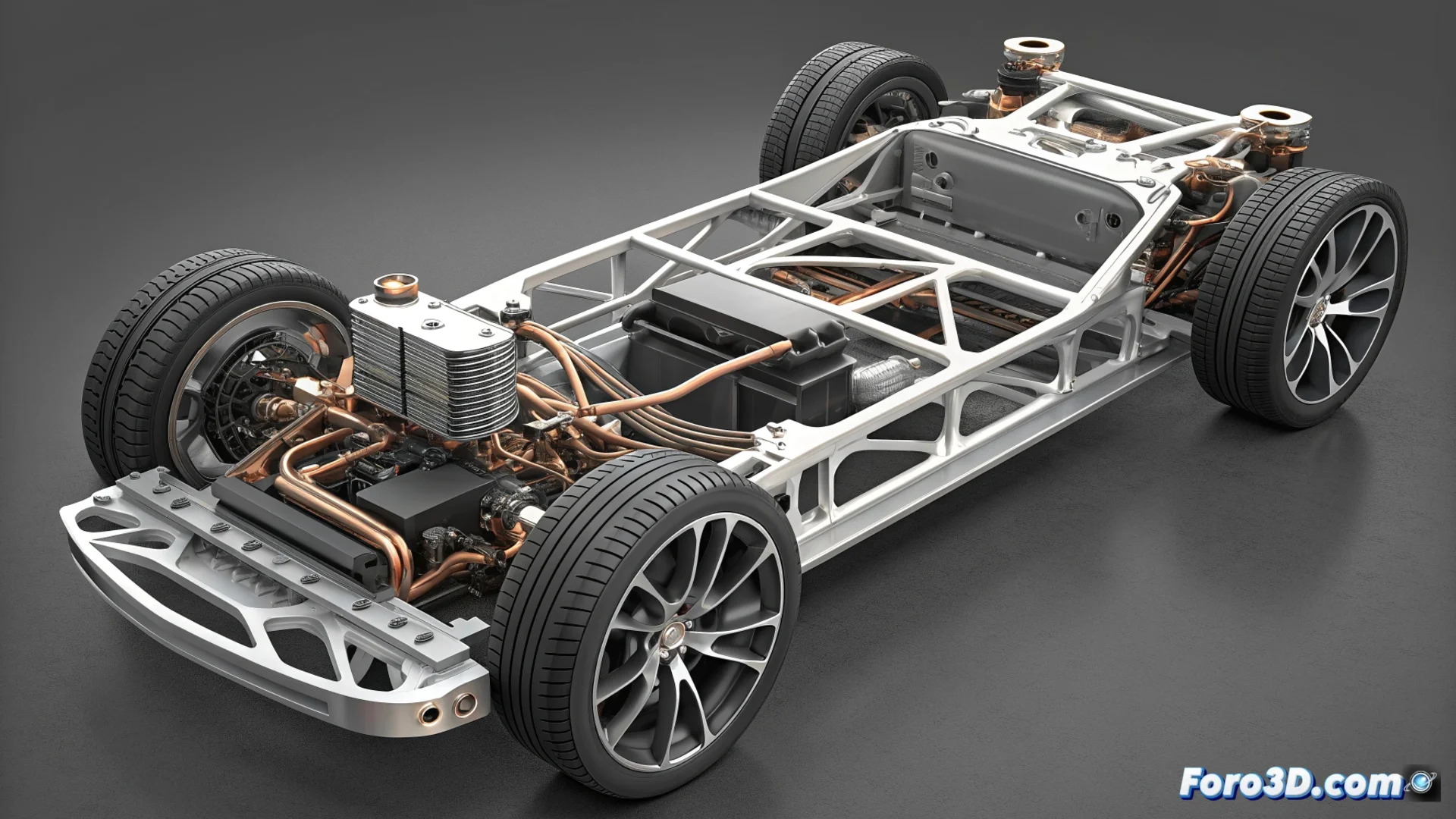
In the sector of electric hypercars, additive manufacturing has become an indispensable tool. The Rimac Nevera integrates this technology to create components that would be unfeasible with conventional methods, thus achieving extreme performance parameters. 🚗⚡
Complex Geometries for Superior Performance
Rimac engineers design parts with intricate shapes that only metal 3D printing can materialize. This approach allows minimizing weight and managing heat optimally, two critical factors in a high-power electric vehicle.
Key Advantages of Additive Manufacturing:- Create support structures with topology optimization, using material only where strictly necessary.
- Produce internal cooling channels with shapes that improve flow and thermal dissipation.
- Consolidate multiple parts into a single printed component, increasing robustness and reducing assemblies.
“Although the cost of printing a single part for this hypercar may exceed that of a family car, the result justifies the process to achieve excellence.”
Printed Engine Mounts: Lightweight and Strong
The Nevera uses mounts to install its four electric motors, manufactured using aluminum 3D printing. This metal offers an excellent strength-to-weight ratio. The technique allows intelligent material distribution, following load lines and eliminating superfluous mass, which translates directly into greater agility and efficiency. 🔩
Features of the Printed Mounts:- Material: High-strength aluminum alloy.
- Objective: Lighten the structure without compromising rigidity.
- Result: Contributes to the vehicle's instant dynamic response.
Thermal Management via Printed Ducts
Controlling temperature is vital for the high-voltage battery and cabin comfort. Rimac manufactures battery cooling ducts and parts of the air conditioning system using aluminum 3D printing. This metal conducts heat well, helping to dissipate the thermal energy generated during fast charges or spirited driving. ❄️
The internal geometries of these ducts are computationally optimized so that the coolant fluid circulates with minimal hydraulic resistance, maximizing the cooling system's efficiency.
The Future of Manufacturing in High-Performance Automotive
The implementation of additive manufacturing in the Rimac Nevera is not just a technological exercise, but a fundamental engineering solution. It demonstrates how this technology enables surpassing design limits, producing components that are lighter, more efficient, and better integrated. Its use, currently focused on extreme-performance vehicles, sets a precedent for the future of electric mobility. 🏁