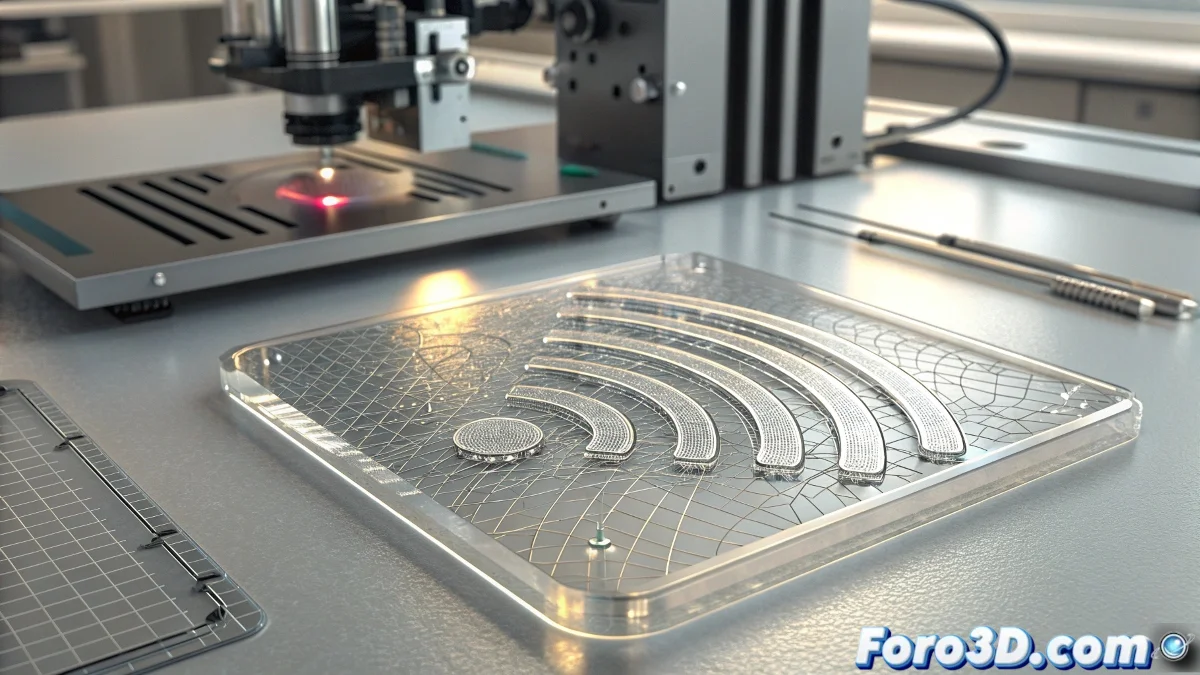
WSU Develops Flexible Antenna Arrays Using 3D Printing for Future Wireless Technologies
Researchers at Washington State University (WSU) have achieved a significant breakthrough in the development of flexible antenna arrays manufactured using advanced 3D printing, specifically designed for future wireless technologies. These antennas represent a fundamental evolution in communication system design, enabling seamless integration into curved surfaces and wearable devices while maintaining exceptional signal performance. The technology promises to revolutionize multiple industries by offering more versatile, durable, and efficient connectivity solutions for applications ranging from wearables to advanced 5G infrastructure. 📡
Flexible Antenna Arrays: Redesigning Connectivity
The WSU-developed antenna arrays represent a paradigmatic shift in radiation system design. Unlike traditional rigid antennas, these arrays maintain their full functionality even when bent, twisted, or adapted to irregular surfaces, opening new integration possibilities in products and environments previously incompatible with conventional antenna technology.
Innovative features of the flexible arrays:- Ability to conform to curved surfaces without performance degradation
- Maintenance of impedance and radiation patterns under mechanical deformation
- Direct integration into device housings and smart textiles
- Possibility of creating conformable arrays for adaptive beamforming
- Significant reduction in weight and volume compared to rigid arrays
- Compatibility with biocompatible materials for medical applications
Flexibility is not just a physical characteristic; it is a fundamental enabler for the next generation of connected devices that will integrate naturally into our environment and clothing.
3D Printing Technology for Antenna Manufacturing
The additive manufacturing process developed by WSU specifically optimizes the production of complex antenna structures that would be impossible or prohibitively expensive with traditional manufacturing methods. 3D printing enables precise micrometric control over geometries critical to radiofrequency performance.
Advantages of 3D printing for antennas:- Manufacturing of complex geometries in a single piece without assembly
- Sub-millimeter precision in features critical for resonance
- Ability to integrate multiple materials with different dielectric properties
- Rapid design iteration with accelerated prototyping cycles
- Cost-effective production of small batches and custom designs
- Minimization of losses due to discontinuities and mechanical connections
Advanced Materials and Improved Durability
WSU researchers have developed specialized polymeric composites that combine exceptional mechanical flexibility with optimized dielectric properties for radiofrequency applications. These materials maintain their structural and electrical integrity even under repeated mechanical stresses. 🔧
Properties of the developed materials:- High flexibility with full recovery capability after deformation
- Dielectric stability across a wide frequency range (up to mmWave)
- Mechanical fatigue resistance for long-term wearable applications
- Low loss tangent for maximum radiation efficiency
- Compatibility with conductive inks for copper and silver patterns
- Dimensional stability under temperature and humidity variations
Applications in Wearables and Portable Devices
The inherent flexibility of these antennas makes them ideal for the next generation of wearable and portable devices. They can be directly integrated into fabrics, bands, and body surfaces without compromising comfort or functionality.
Specific wearable applications:- Smart clothing with integrated communications for health monitoring
- Wearable medical devices with continuous and reliable connectivity
- Sports equipment with real-time telemetry
- Augmented and virtual reality with integrated communication systems
- Location and tracking devices for personal safety
- Portable environmental sensors with wireless data transmission
Optimization for 5G and Millimeter-Wave Frequencies
The WSU-developed arrays are specifically optimized to operate in 5G and beyond frequency bands, including the millimeter-wave (mmWave) range where traditional antennas face significant efficiency and integration challenges.
Features for 5G/mmWave applications:- Designs optimized for FR2 bands (24-71 GHz) with high efficiency
- Multi-element arrays for beamforming and advanced MIMO
- Low-latency manufacturing for rapid iteration of specific designs
- Integration with low-loss substrates for maximum gain
- Compatibility with diverse polarization techniques to improve robustness
- Ability to create reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (RIS)
Advantages Over Traditional Manufacturing Methods
3D printing of antenna arrays offers substantial competitive advantages compared to conventional manufacturing methods such as PCB etching or machining, particularly for applications requiring customization, geometric complexity, or conformal integration.
Comparison with traditional methods:- 70% reduction in functional prototype development time
- 60% decrease in tooling and manufacturing setup costs
- Ability to produce complex 3D geometries impossible with flat PCBs
- Integration of passive components and antenna structures in a single process
- Minimization of losses due to interconnections and impedance adapters
- Possibility of distributed and on-demand manufacturing
Impact on Industries and Future Applications
The technology developed at WSU has far-reaching implications for multiple industrial sectors and emerging applications, from the Internet of Things (IoT) to mission-critical communications.
Transformed industries and applications:- Telecommunications: 5G base stations with conformal arrays
- Automotive: V2X communication systems integrated into vehicle bodies
- Aerospace: Lightweight antennas conformed to aircraft surfaces
- Healthcare: Implantable and wearable medical devices for continuous monitoring
- Smart Cities: Environmental sensors integrated into urban infrastructure
- Defense: Robust communication systems for personnel and vehicles
Conclusion: Connectivity Without Physical Limits
The development of flexible antenna arrays using 3D printing by Washington State University represents a transformative milestone in the evolution of wireless technologies. By eliminating the traditional physical constraints of antenna design, this technology not only improves performance and reduces costs, but radically expands integration possibilities for communication capabilities into virtually any surface or object. As we advance toward an increasingly connected world, where ubiquitous and seamless communication becomes a fundamental expectation, innovations like this will be critical to enabling the next generation of digital applications and services. The synergistic combination of advanced 3D printing, specialized flexible materials, and optimized electromagnetic design lays the foundation for an era of truly omnipresent connectivity that will integrate naturally into our daily environment. 🌐