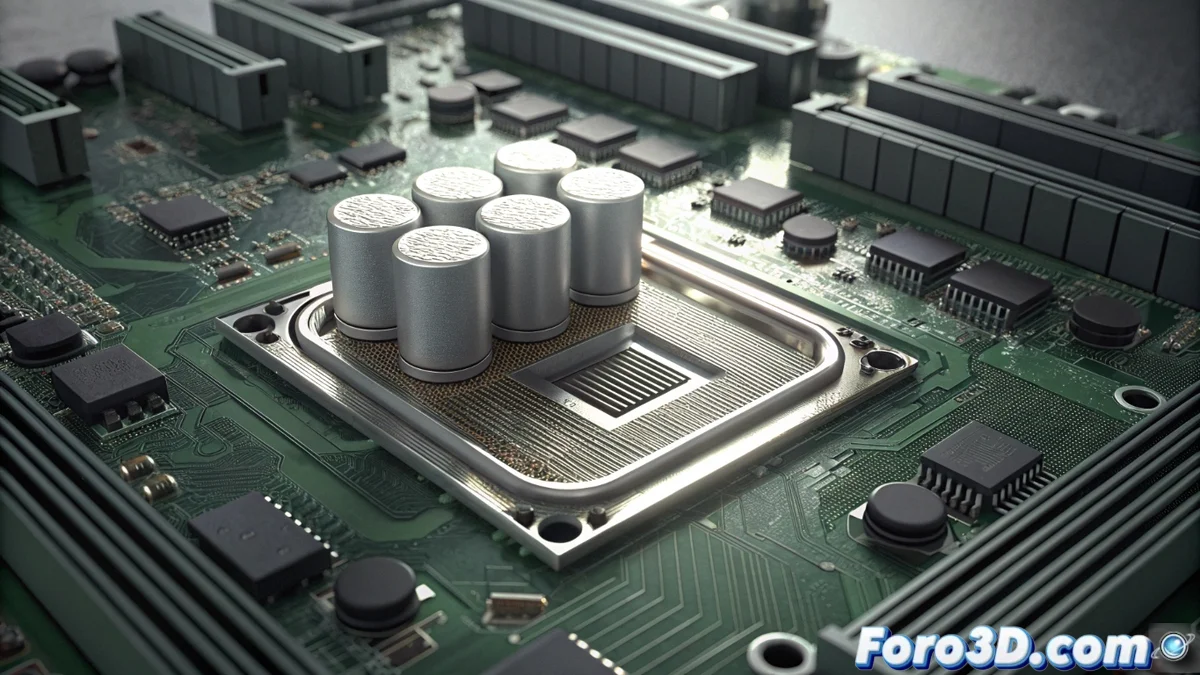
What is a VRM and why is it key to your motherboard
At the heart of any powerful computing system, the Voltage Regulator Module (VRM) acts as the precision power supplier. Its main task is to transform the raw 12-volt power coming from the power supply into a low, stable, and precise voltage flow that microprocessors like the CPU or GPU demand to operate. Without this component, modern chips simply couldn't function reliably. ⚡
The phased architecture: the secret to power and stability
A VRM is not a single circuit, but a system organized into power phases. Imagine each phase as an independent lane that shares the load of delivering current. The more lanes (phases) it has, the better the work is distributed. This allows each individual component to operate cooler and more efficiently, resulting in a cleaner power signal. For users who demand maximum performance or practice overclocking, a design with many phases is crucial, as it prevents the system from saturating and overheating, avoiding crashes and failures.
Advantages of a VRM with more phases:- Distributes the electrical load and generated heat across more components.
- Allows each element to work at a lower temperature, increasing its lifespan.
- Delivers more stable power during intense workloads or when increasing voltage.
A robust VRM doesn't make a slow processor fast, but it ensures that any processor receives power in the most efficient and stable way possible.
The components that define VRM quality
A VRM's capability depends directly on the quality of its fundamental parts. Each phase is built around three key elements. The MOSFETs act as high-speed switches, regulating voltage by opening and closing the current flow thousands of times per second. The inductors or chokes store energy and smooth the current, while the capacitors filter the final signal to eliminate any residual variation. Using high-end components here makes the difference, as they can handle higher currents and dissipate heat more effectively, often with the help of metal heatsinks.
Key elements in each power phase:- MOSFETs: High-frequency switches that regulate voltage. Their quality defines efficiency and thermal limit.
- Inductors (Chokes): Store energy and help smooth the electrical current flow.
- Capacitors: Filter the output signal to achieve a flat current free of fluctuations.
Why you should pay attention to it
Choosing a motherboard or graphics card with a well-designed VRM is an investment in system stability and longevity. It ensures that your processor, whether mid-range or high-end, operates within its ideal voltage parameters under any load. This is especially valuable if you plan to optimize your hardware's performance, as a weak VRM will be the first limit you encounter. In summary, a good voltage regulator is the invisible but essential foundation on which a powerful and reliable computing system is built. 🛡️