The Challenge of Digital Independence in Hand Rigging
Experiencing fingers moving involuntarily when rotating the torso or wrist is like having puppets with crossed strings 🎭. This common problem in complex rigs occurs when well-intentioned stretch, follow, or constraint systems end up creating unwanted connections between body parts that should remain independent. The solution requires understanding the rig's architecture and applying intelligent filters.
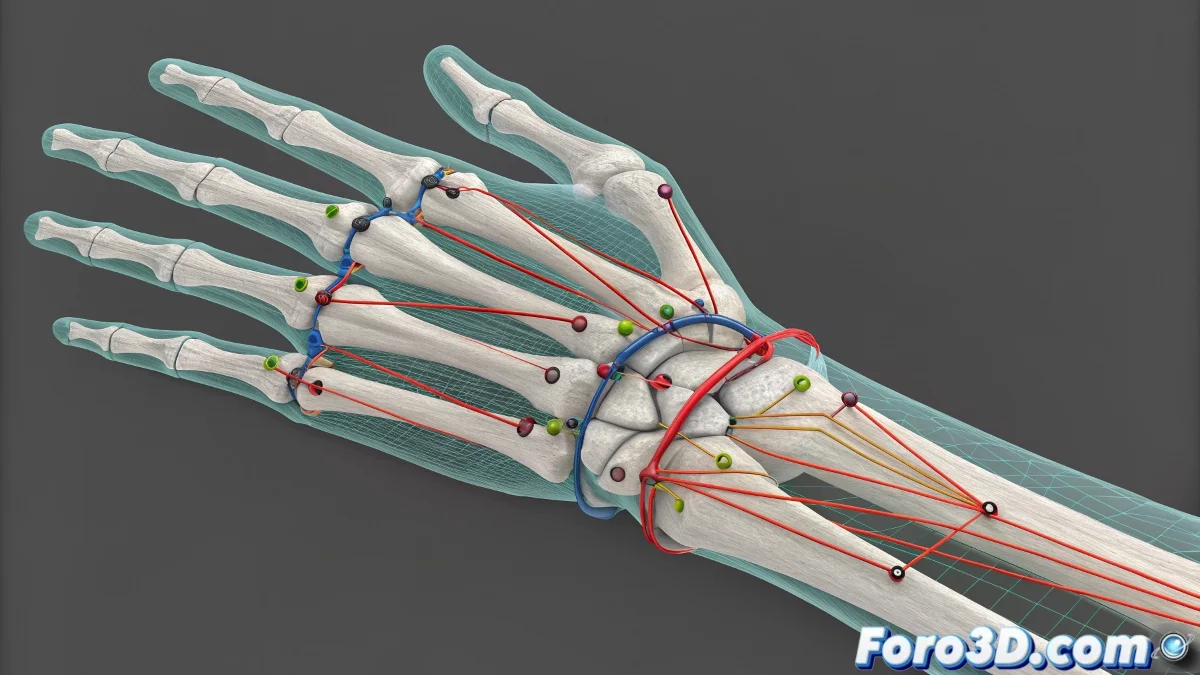
Anatomy of a Propagation Problem
The root of the problem usually lies in constraints that transmit transformations across multiple hierarchical levels. A small movement in the chest can be amplified through the arm's stretch system and end up affecting finger controllers that should only respond to their own controls.
A well-isolated rig is like an orchestra: each section plays its score without interfering with the others.
Isolation and Filtering Techniques
Several technical approaches allow isolating finger controllers from unwanted movements coming from other parts of the rig.
- Strategic reparenting: Reorganize hierarchies for independence
- Constraint weight adjustment: Adjust influence weights to minimize propagation
- Group offsets: Create intermediate groups to absorb transformations
- Space switching: Allow switching between different reference spaces
Using Condition Nodes for Intelligent Control
Condition nodes act as digital gatekeepers that only allow the passage of transformations meeting specific criteria.
- Distance thresholds: Only activate stretch beyond a certain distance
- Angular limits: Filter rotations outside the desired range
- Operation modes: Allow different behaviors depending on the context
- Controlled blending: Smooth interpolation between different states
Transform Limits as Containment Barriers
Transform limits act as physical barriers that prevent values from propagating beyond established thresholds.
- Translation limits: Contain movement within specific areas
- Rotation limits: Restrict rotations to anatomically possible ranges
- Scale limits: Prevent extreme compression or stretching
- Soft limits: Restrictions that allow some flexibility near the limits
Review and Debugging of Existing Constraints
When propagation problems appear, a systematic debugging approach helps identify and resolve problematic connections quickly.
- Hypergraph examination: Visualize all connections between nodes
- Constraint isolation: Temporarily disable constraints to identify culprits
- Value monitoring: Observe how values propagate through the system
- Incremental testing: Test small changes and verify results
Preventive Design for Future Rigs
The best solution is always to prevent these problems through proper architectural design from the initial rigging stages.
And when your fingers still move like possessed by digital spirits, you can always argue it's an advanced neuromuscular realism feature 👻. After all, in the rigging world, sometimes persistent bugs become the character's personality features.