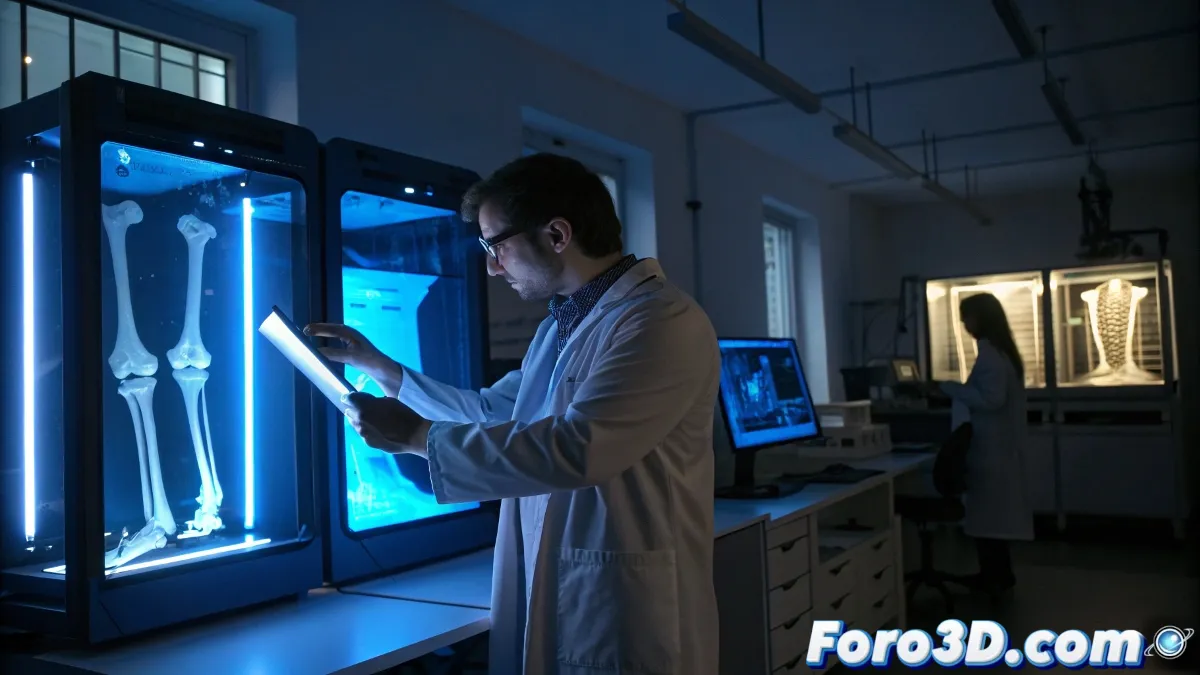

Advancement in Biofabrication of Bone Structures
An Australian research group has developed an additive manufacturing method that reproduces bone tissue with nanometric precision. This technology allows control of key structural parameters such as pore size and mineral distribution, achieving resolutions of 300 nanometers. The approach represents a qualitative leap in the creation of artificial bone substitutes.
Bio-printing Technology
The system employs a special formulation based on mineral components analogous to those present in natural bone. The fundamental innovation consists of:
- Use of biological nucleation precursors
- Transparent resin matrix for optical control
- Optimization of microscale printing parameters
"The reproduction of structural features at the nanometric level is crucial for the biological integration of implants"
Clinical Advantages
Compared to traditional implants, this development offers significant benefits. The porous structure facilitates vascularization and allows progressive bone remodeling. Additionally, the chemical composition of the material stimulates natural tissue regeneration processes.
Potential Medical Applications
The technology could revolutionize the treatment of:
- Complex bone defects
- Traumatic substance losses
- Joint reconstructions
- Reconstructive orthopedic surgeries
The researchers are currently focused on scaling the process while maintaining critical nanoscale features. Technology transfer to clinical settings will require additional validations, but preliminary results suggest transformative potential in the field of regenerative medicine.