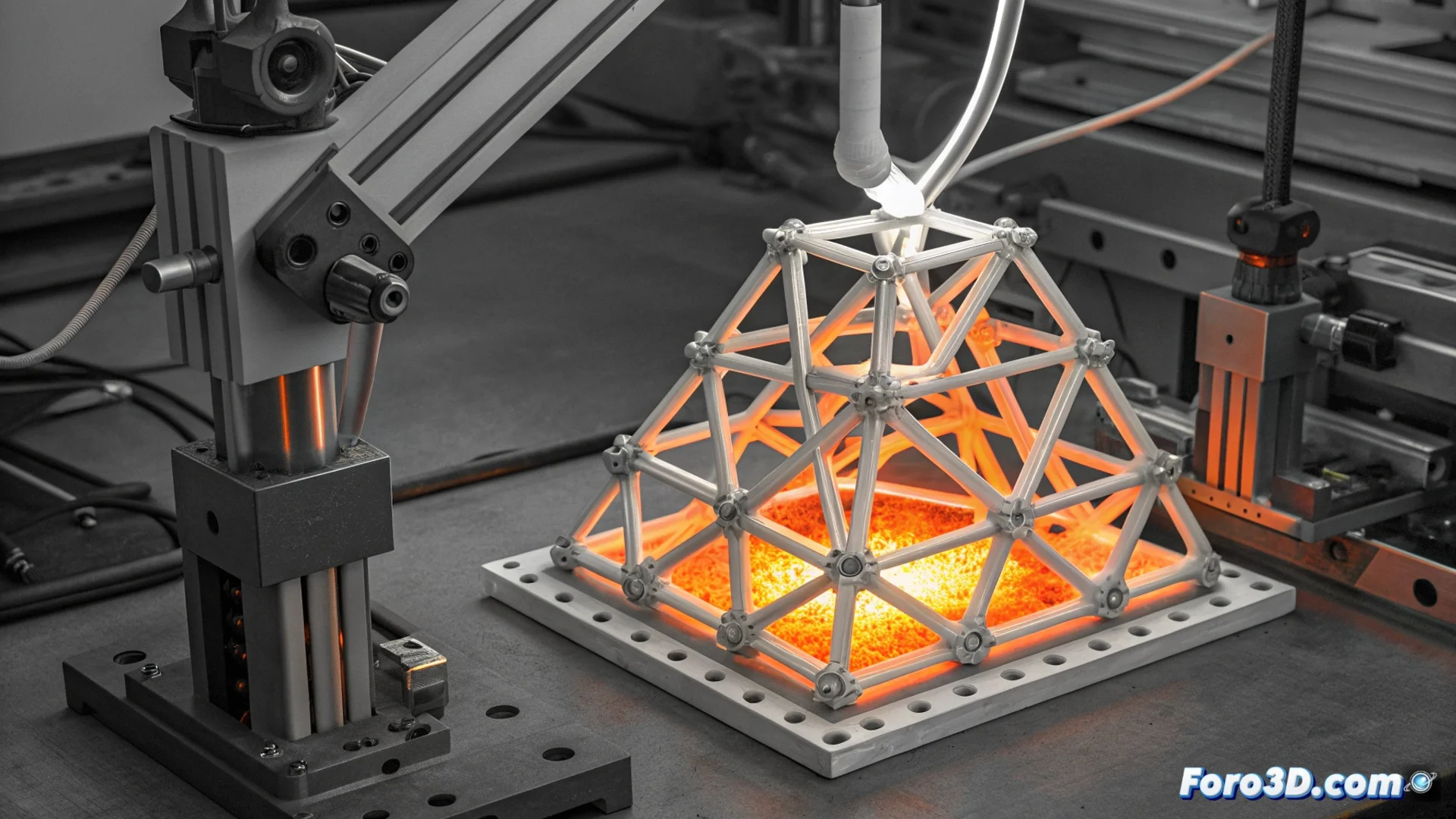
Researchers Create a Ceramic-Metal Composite with Shape Memory for 3D Printing
A team of scientists from Virginia Tech University has successfully developed a new hybrid material designed for manufacturing via 3D printing. This innovative composite fuses the properties of ceramics and metal, endowing the produced objects with remarkable shape memory. 🧠
Processing the Material with Additive Manufacturing
To produce components with this material, the team uses an additive manufacturing method based on stereolithography. This process utilizes a special liquid resin containing a suspension of ceramic particles and a shape memory alloy. Ultraviolet light solidifies the resin layer by layer, resulting in a "green" part.
Key Steps After Printing:- Thermal Treatment: The printed part is heated to remove the polymer binder and consolidate the structure.
- Sintering: The metallic and ceramic particles fuse, resulting in a solid, fully dense final component.
- Shape Programming: The material can "learn" an initial configuration that it will be able to remember and recover.
Combining the temperature resistance of ceramics with the shape memory properties of metal overcomes key limitations of other materials.
Where to Apply This Technological Breakthrough
The unique combination of properties opens up a range of potential applications in industries operating under extreme conditions. The material's ability to withstand high temperatures and change shape in a controlled manner is its main advantage.
Highlighted Application Fields:- Aerospace Sector: To create components that deploy autonomously in space or actuators for satellite systems. 🛰️
- Biomedicine: In the design of smart devices for controlled drug release inside the human body.
- Advanced Electronics: To manufacture parts in devices that need to be lightweight and thermally stable.
The Future of Smart Materials
This development represents