Revival of Larval Therapy in Modern Medicine
Biocurgery is experiencing a notable resurgence with the medical application of fly larvae for the treatment of complex wounds. These organisms, technically known as biological debridement agents, represent an ancestral solution that is regaining relevance in contemporary medicine 🩹.
Therapeutic Mechanisms of Medicinal Larvae
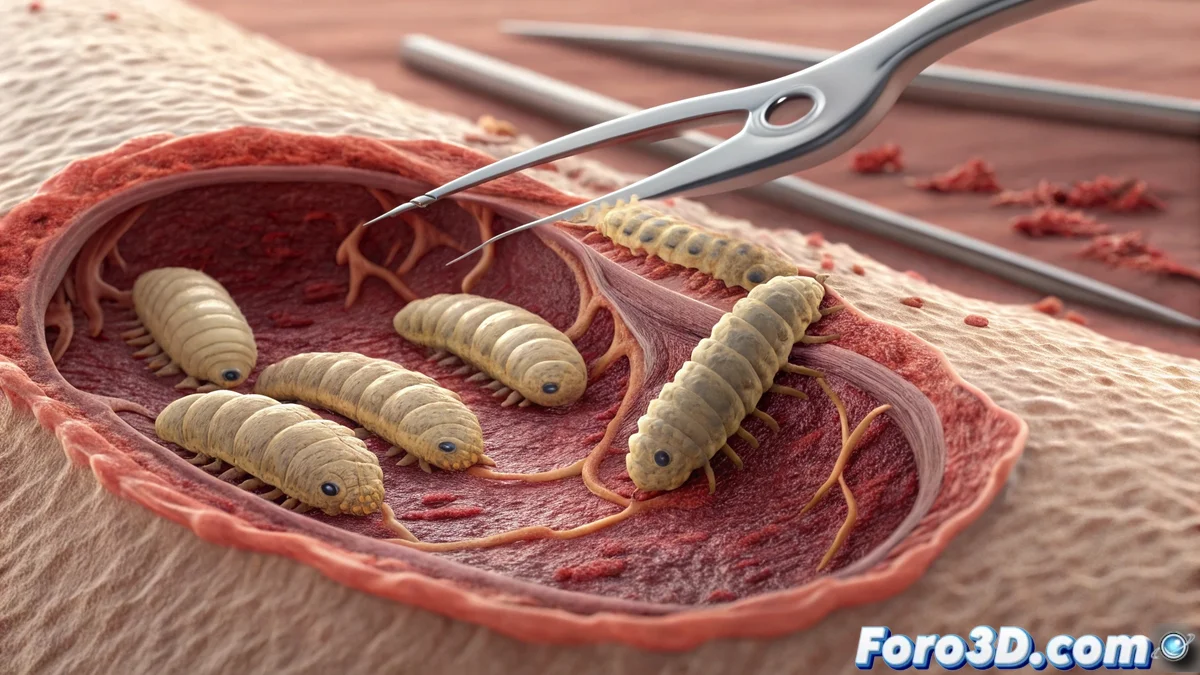
Sterile larvae exert their beneficial action through three fundamental mechanisms: they selectively consume necrotic tissue, secrete enzymes that dissolve devitalized material, and produce antimicrobial substances that control infections. This larval therapy is particularly valuable in patients with chronic ulcers that do not respond to conventional treatments.
Advantages of Biological Debridement:- Precise removal of dead tissue without damaging adjacent healthy structures
- Significant reduction of bacterial load in infected wounds
- Stimulation of natural healing and granulation processes
The larva is the most precise surgeon that exists, capable of distinguishing millimeter by millimeter between viable and necrotic tissue without the need for anesthesia
Safety Protocols in Clinical Application
The handling of these therapeutic worms requires strict containment and sterilization protocols. Professionals use specialized dressings that prevent the escape of the larvae while allowing necessary oxygenation. The selection of species such as Lucilia sericata is crucial, as other varieties could introduce pathogens or behave invasively.
Essential Control Measures:- Prior sterilization of eggs using validated methods
- Physical containment systems with calibrated pore mesh
- Continuous monitoring during the treatment period
Implications for Public Health and Surveillance
The potential escape of these larvae into the environment represents a considerable epidemiological risk. Adult flies can lay eggs in open wounds of humans and animals, with the larvae developing in living tissues and causing myiasis. Health authorities maintain active surveillance and vector control programs, particularly in regions with deficient hygienic-sanitary conditions.
Final Considerations on Larval Therapy
Although these healing worms demonstrate remarkable efficacy in managing complex wounds, their application must be strictly limited to the controlled clinical setting. The very property that makes them valuable in medicine—their ability to develop in tissues—turns them into a significant risk if they escape to unsupervised environments. Biocurgery thus represents a fascinating example of how natural solutions can be responsibly integrated into modern medical practice 🪰.