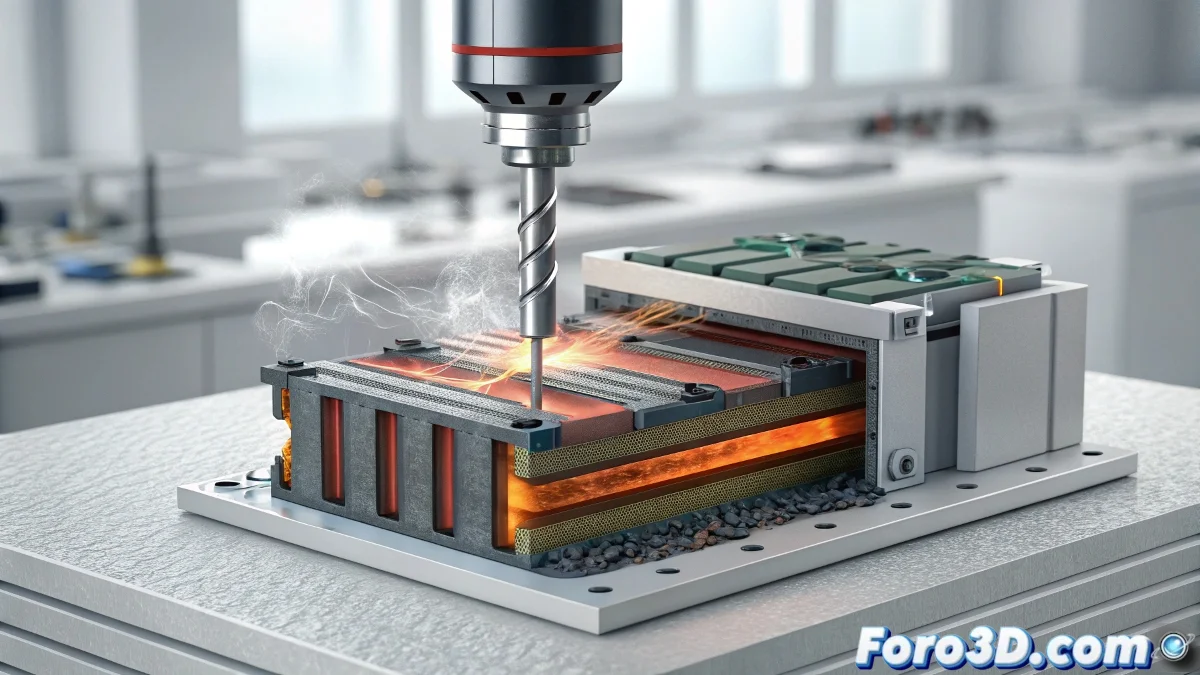
Lithium-Ion Batteries Resistant to Puncture-Induced Fires Improve Safety in Electric Mobility
Electrochemical safety reaches a crucial milestone with the development of lithium-ion batteries that maintain their integrity even when punctured. This innovation in materials engineering effectively prevents the dreaded thermal runaway fires, addressing one of the main concerns in electrification 🔋.
Redesigned Internal Architecture for Fault Containment
The multi-level approach combines advanced ceramic separators, electrolytes with flame-retardant additives, and passive thermal management systems. These synergistic components create physical and chemical barriers that interrupt the chain reaction before it reaches critical self-accelerating temperatures.
Critical Modifications Implemented:- Nanocomposite separators that thermally expand, sealing micro-cracks
- Electrolytes with flame retardants that activate at 150°C
- Cathode structures that minimize oxygen release during overheating
We have transformed the response to physical damage from catastrophic to manageable, creating a battery that can fail safely
Impact on Electric Vehicle and Device Safety
The tolerance to mechanical damage has direct implications for occupant safety in electric vehicle collisions and for the integrity of portable devices in demanding environments. This inherent resistance could dramatically reduce reported incidents of spontaneous fires 🔥.
Safety Test Results:- Zero open flames in 3mm nail penetration tests
- Fault containment to the damaged cell without thermal propagation
- Maximum temperature controlled below 300°C during puncture
Path to Commercial Implementation
Despite the demonstrated technical advancement, the challenge of industrial scalability and cost optimization remains. Researchers are working to balance the safety premium with the economic viability necessary for mass adoption in competitive markets 🏭.