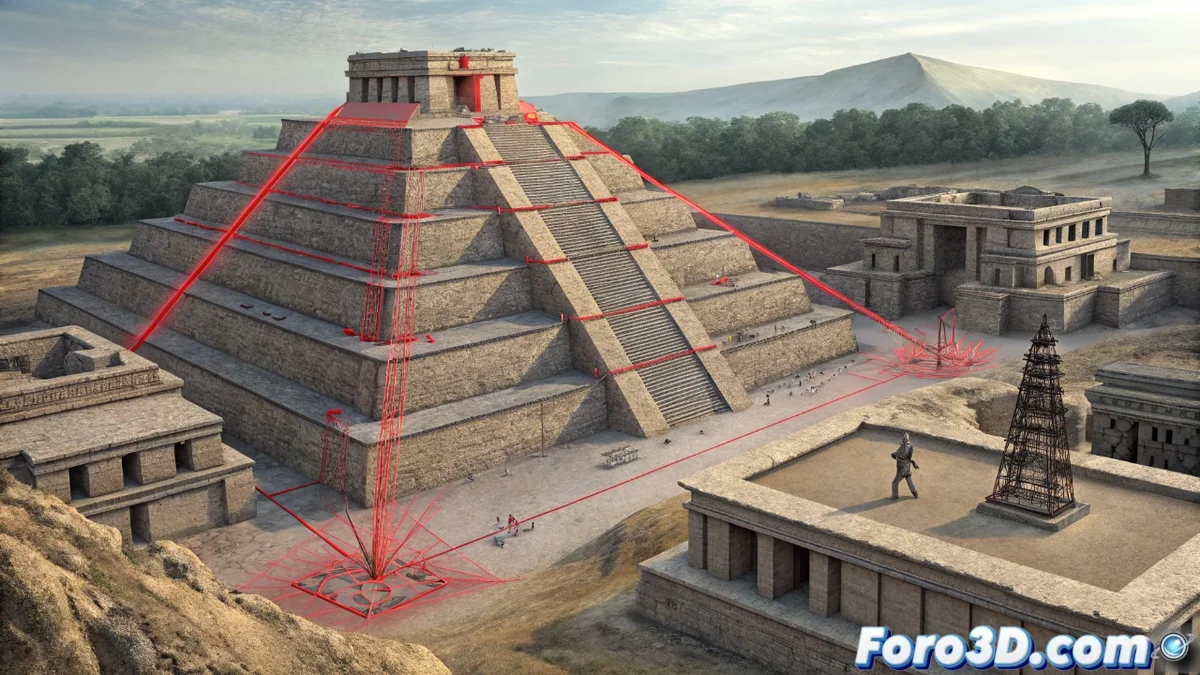
Incremental Learning Revolutionizes 3D Modeling with Continuous Updates
The incremental learning methodology is radically transforming three-dimensional creation workflows, enabling real-time updates without the need to restart projects from scratch. This paradigm is particularly valuable in disciplines such as architectural reconstruction and complex archaeological projects, where each new iteration integrates additional information while preserving the structural integrity of previous versions. 🚀
Intelligent Automatic Verification Mechanisms
Each modification in the model activates validation protocols that examine specialized metrics such as polygonal density, topological precision, and preservation of surface details. The systems implement differential comparison algorithms capable of identifying resolution losses in architectural decorative elements or alterations in archaeological strata. The technology enables targeted corrections in conflicting areas without affecting already validated regions, significantly optimizing processing times.
Main Features of Validation Systems:- Comparative analysis between consecutive model versions
- Automatic detection of structural and geometric discrepancies
- Selective intervention capability in problematic sectors
The true innovation lies in how these systems maintain the project's historical coherence while incorporating recent discoveries
Applications in High-Complexity Environments
In reconstructions of natural landscapes, incremental learning manages the integration of new LiDAR data while preserving existing geomorphology. For archaeological contexts, the system maintains intact stratigraphic records even when recent findings are incorporated. The methodology demonstrates special effectiveness in heritage restoration projects, where historical documentation and contemporary scans must coexist without geometric contradictions.
Specialized Application Fields:- Reconstruction of natural landscapes with LiDAR data
- Archaeological projects with complex stratigraphy
- Restoration of architectural and historical heritage
Final Reflections on the Technology
It is paradoxical how these systems can detect minimal errors in three-dimensional models with millimeter precision, yet still fail to solve the universal mystery of why critical files always disappear just before final deliveries. The continuous evolution of these tools promises to further revolutionize modeling processes, making three-dimensional work more efficient and reliable. 🔍