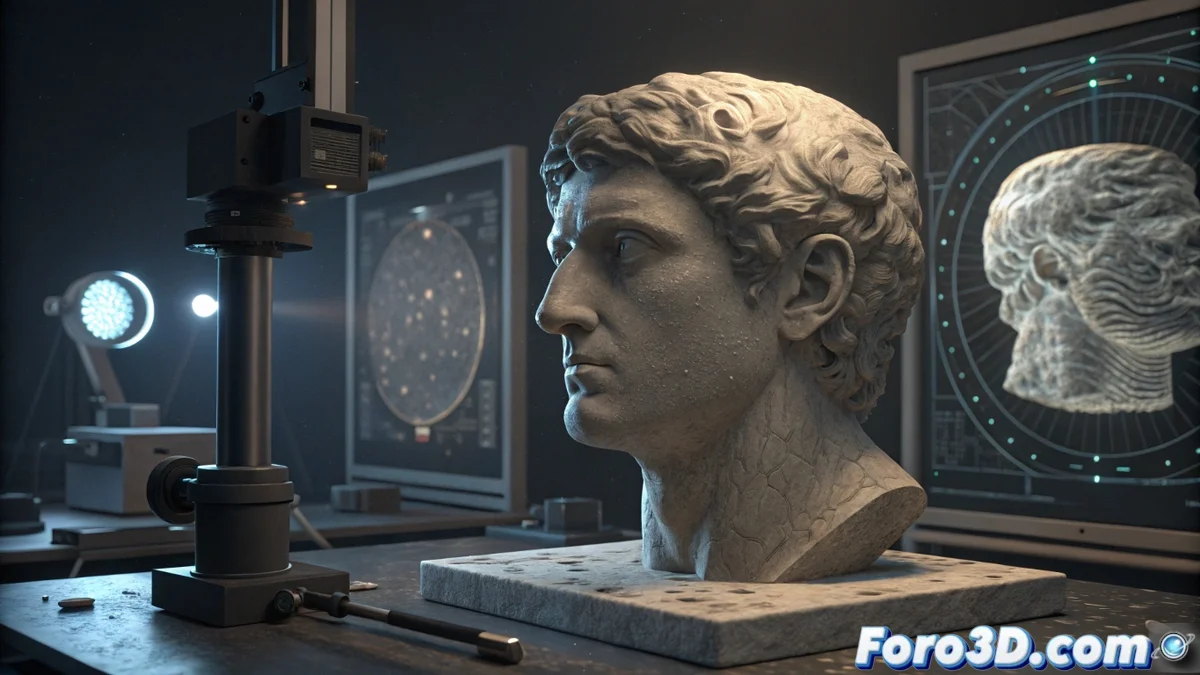
Forensic Authentication of Roman Sculpture Using 3D Scanning
Contemporary museum institutions face the daily challenge of verifying the authenticity of their archaeological acquisitions. In this context, a marble head attributed to the Roman era enters the collections under strict validation protocols that combine cutting-edge technology with scientific methodology 🔍.
Comprehensive Digitization with Advanced Systems
The investigative process begins with an ultra-high-precision three-dimensional capture using the GOM ATOS | Creaform HandySCAN system, which employs structured light technology to record even the smallest surface imperfections. This comprehensive digitization allows documenting the manufacturing traces with a level of detail unattainable by conventional techniques, laying the foundations for subsequent forensic comparative analysis.
Key features of the scanning process:- Micrometric resolution that captures textures invisible to the human eye
- Complete documentation of striations, blows, and characteristic wear
- Creation of digital models suitable for advanced metrological analysis
3D technology allows us to read the fingerprints of ancient artisans on the marble surface, revealing secrets that had been hidden for centuries.
Forensic Analysis of Carving Techniques
Once the high-fidelity digital model is obtained, specialists use specialized software like GOM Inspect | PolyWorks to examine the microscopic characteristics of the sculptural surface. The main focus is on the tool marks left by chisels, gouges, and other carving tools, which function as a unique identifying fingerprint of each historical workshop or artisan.
Forensic comparison methodology:- Systematic comparison with databases of authentic Roman tools
- Search for stylistic matches and characteristic work patterns
- Detection of technological anachronisms that evidence forgeries
Advanced Visualization and Final Verdict
To optimize the interpretation of evidence, ZBrush is used to enhance and controllably exaggerate surface textures, transforming subtle variations into clearly discernible patterns. This controlled amplification allows experts to identify even the most minimal discrepancies in direction, depth, and morphology of the marks, contrasting them with the documented historical standards of the attributed period and workshop. The process concludes with a definitive expert report that determines the authenticity or falsity of the piece based on irrefutable technical evidence 📊.
Sculptures often reveal more information under the 3D scanner than after centuries displayed in museum cases, demonstrating that even the oldest marble can hide quite questionable modern stories that only contemporary technology can fully uncover 💡.