Diagnose and Troubleshoot Axes and Sensors in 3D Printers
Accuracy in 3D printing is based on the proper functioning of the components that control movement. When the mechanical axes or position sensors show anomalies, the machine loses fidelity and the parts exhibit imperfections. These errors often arise from natural wear, poor assembly, or electrical noise that corrupts signals. Detecting the precise origin is the initial step to correct it and return to printing with quality. 🔧
Inspect and Correct Mechanical Components
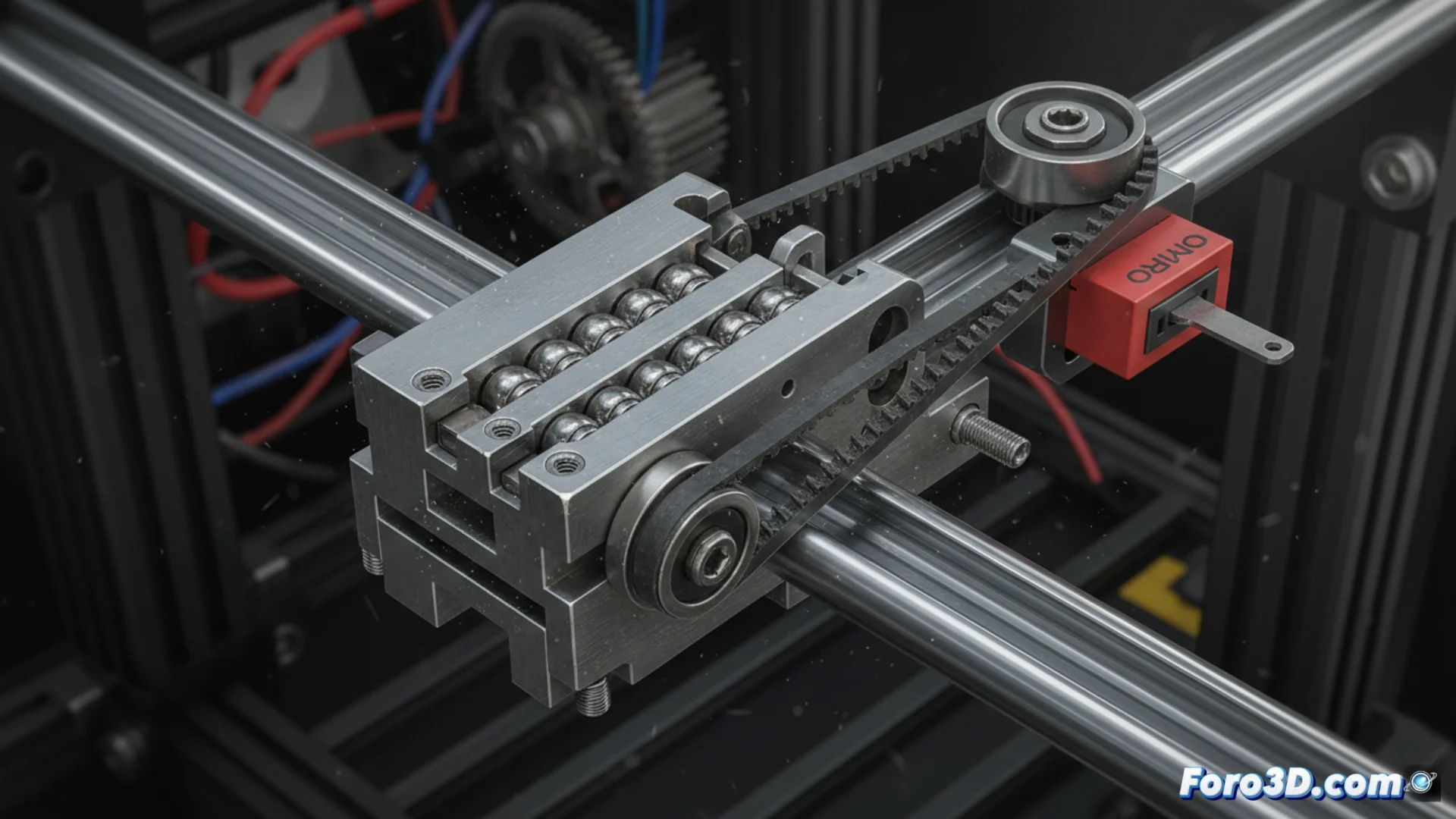
Over time, linear guides, rods, and drive belts can lose their alignment or proper tension. A structure with play transmits vibrations and generates visible artifacts in the final object. It is crucial to verify that all fastening elements, such as nuts and clamps, are firmly tightened. Additionally, it is recommended to clean and lubricate the guides periodically to prevent them from seizing and causing jumps in movement, which results in misaligned layers.
Essential mechanical maintenance actions:- Adjust all connections and supports to eliminate play.
- Clean linear guides and apply specific lubricant regularly.
- Check the correct tension of the belts to avoid slippage.
The machine doesn't lie; it simply executes incorrect instructions. Sometimes the problem is not in the firmware, but in a simple screw that needs tightening.
Identify and Repair Sensor Failures
Endstop detectors and encoders can stop operating correctly due to dust accumulation or faulty electrical connections. A sensor that does not read accurately causes the head to impact physical limits or the printer's origin point to be incorrect. To fix it, the sensor's detection area must be cleaned and the wiring integrity examined. When there are electromagnetic interferences, it may be necessary to shield the cables or install a filtering capacitor to clean the electrical signal.
Steps to troubleshoot sensor issues:- Clean the optical or mechanical area of the endstop sensor.
- Inspect and secure wiring connectors and terminals.
- Implement interference filters, such as capacitors or shielding.
Systematic Approach to Recover Precision
Restoring optimal performance of a 3D printer requires an orderly method. First, the mechanical integrity must be inspected. Then, evaluate the condition of the sensors and their electronics. Many printing defects, such as shifted layers or inaccurate dimensions, are resolved by addressing these physical elements before modifying software settings. Constant preventive maintenance is the best strategy to avoid these failures and keep the machine producing with maximum fidelity. 🛠️