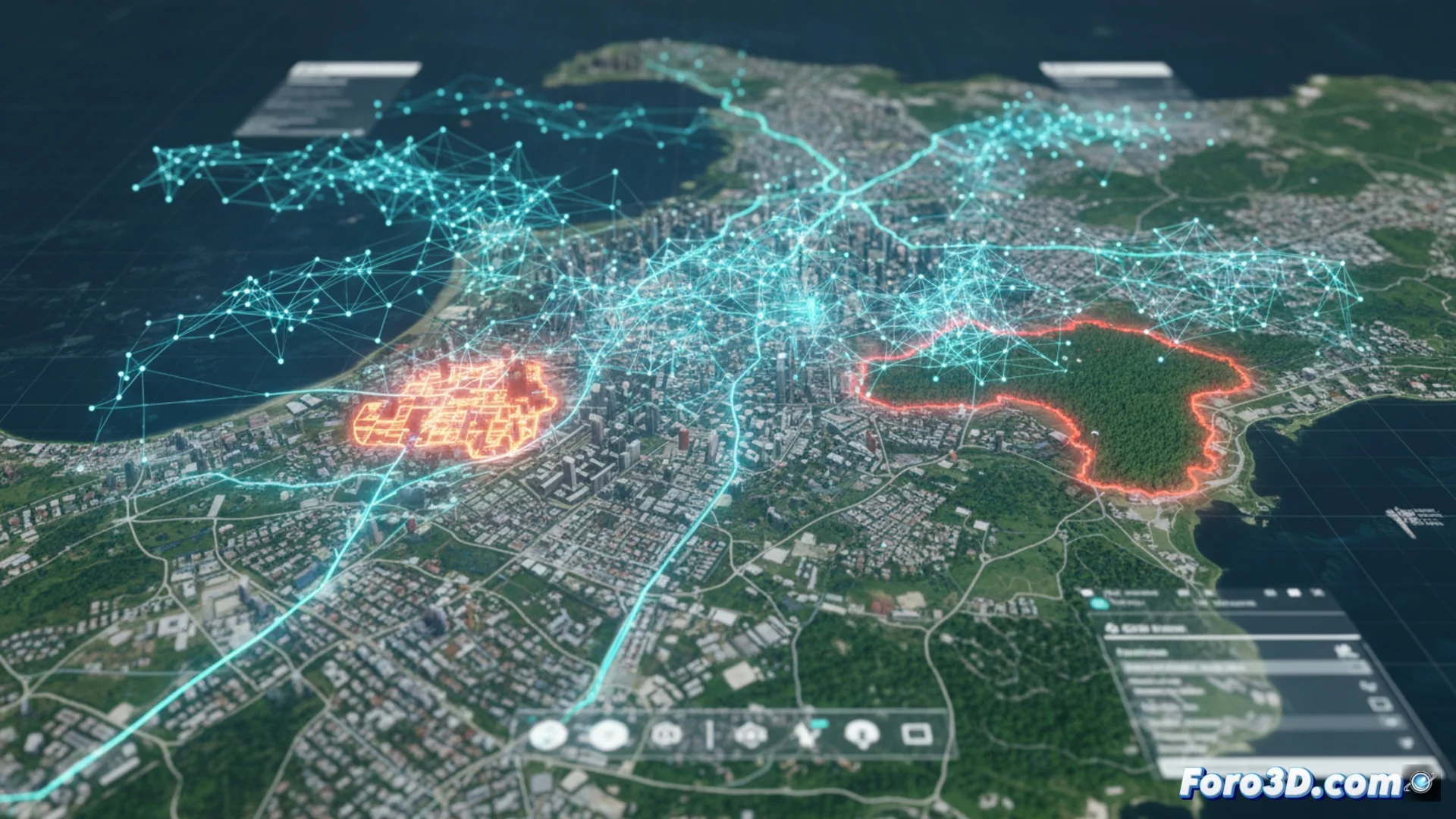
ArcGIS GeoAI Combines Artificial Intelligence and Spatial Data
The ArcGIS GeoAI platform fuses artificial intelligence methods with georeferenced information to obtain insights more effectively. This solution enables automatic examination of aerial or satellite photographs, recognition of complex structures in large datasets, and creation of location-based forecasts. Experts use these utilities to catalog terrain types, detect landscape alterations, and simulate natural events or urban environments. The system incorporates preconfigured models and provides a space to build custom applications, simplifying the use of machine learning and deep learning algorithms without requiring extensive coding expertise. 🧠
Practical Uses in Various Professional Fields
The functions extend to multiple industries. In the environmental sector, it serves to monitor forest loss, calculate impacts after disasters, or track plantation status. For city design and infrastructure management, it helps locate unregulated housing, enumerate constructions, or predict metropolitan area expansion. In distribution and mobility, algorithms improve delivery routes and forecast high-traffic zones. It is also used in civil protection to examine event trends or in advanced agriculture to manage water and nutrients. The ability to handle past and live data adds a key temporal dimension to studies.
Sectoral Implementation Examples:- Environment: Track crop health and assess post-disaster damage.
- Urban Planning: Identify settlements and predict city growth.
- Logistics: Optimize delivery routes and congestion areas.
The ability to process historical and real-time data endows analyses with a crucial temporal dimension.
Methodology for Working with Specific Tools
The process typically begins in ArcGIS Pro, where source data is prepared, such as multi-band images or vector data collections. Then, GeoAI functions are used within the Image Analyst or Spatial Analyst modules to train models, such as convolutional neural networks, or perform inferences with existing models. ArcGIS API for Python enables process automation and integration of libraries like TensorFlow or PyTorch. Outputs, such as polygons of located features or probability maps, are displayed and shared through portals like ArcGIS Online or ArcGIS Enterprise, streamlining collaborative decision-making.
Key Workflow Components:- Data Preparation: Use ArcGIS Pro to organize multispectral images and vector datasets.
- Training and Inference: Apply Image/Spatial Analyst tools for neural network models.
- Automation and Deployment: Use ArcGIS API for Python with TensorFlow/PyTorch and share results on online portals.
Considerations and Future Perspectives
When applying these systems, misinterpretations may occasionally arise, such as confusing a large shopping center with a forested area, possibly due to similarities in certain visual patterns. This underscores the importance of continuously validating and fine-tuning models. The evolution of GeoAI continues to expand its capacity to transform raw spatial data into actionable knowledge, democratizing the use of geospatial AI so more professionals can solve complex problems without relying exclusively on programming specialists. The future points to more accurate models and even smoother integration into daily cartographic workflows. 🗺️