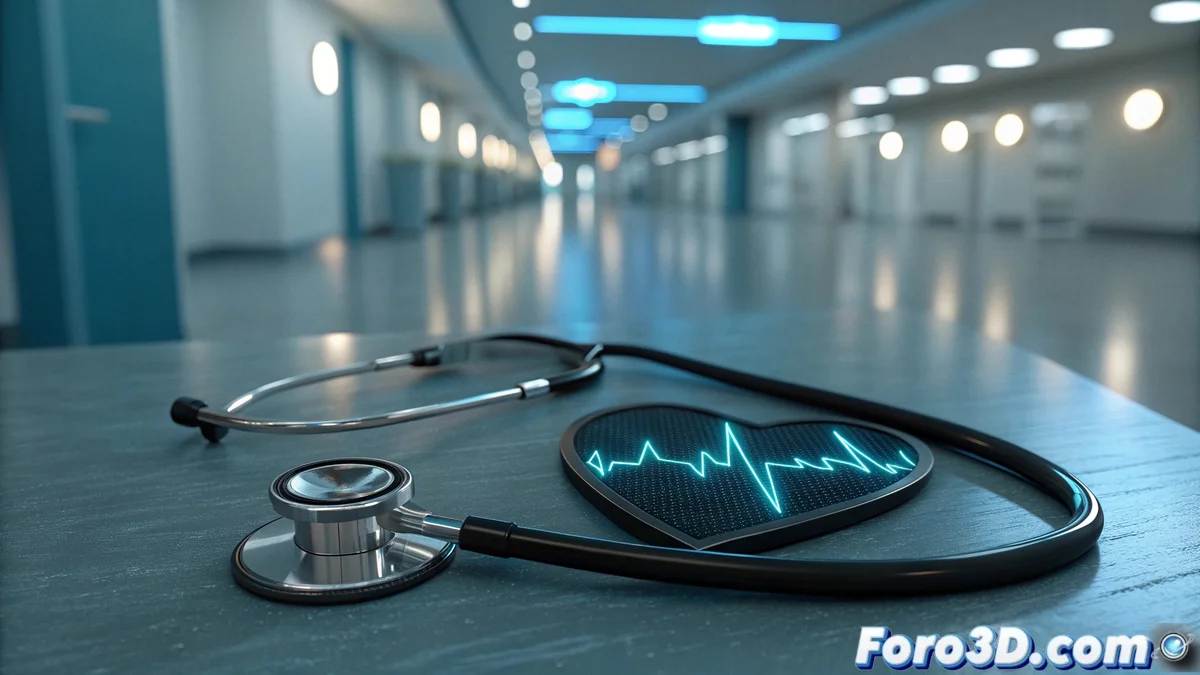

When Artificial Intelligence Listens to the Heart
A team of researchers has developed a smart stethoscope capable of analyzing heart sounds and detecting possible heart damage using artificial intelligence algorithms. This technological innovation promises to revolutionize early diagnosis and healthcare, especially in rural settings or areas with limited access to cardiologists. The device combines the centuries-old medical tradition of the stethoscope with the power of modern machine learning. 🩺
Advanced Detection Using Intelligent Algorithms
The device uses machine learning models to recognize abnormal patterns in heartbeats, identifying murmurs, arrhythmias, or heart valve damage with greater accuracy than a trained human ear. The AI compares the captured sounds with extensive patient databases and determines the probability of various conditions, providing the doctor with valuable complementary information to establish more accurate diagnoses.
Significant Advantages in Healthcare
This smart stethoscope enables more precise cardiac examinations without the need for complex or expensive additional equipment. Its portability and ease of use greatly facilitate the work of doctors in rural clinics, emergency services, or practices with limited resources, accelerating the identification of critical problems and improving real-time medical decision-making.
- Early Diagnosis: Early detection of asymptomatic cardiac conditions.
- Improved Accessibility: Cardiology care in remote areas.
- Error Reduction: Objective analysis complementary to medical judgment.
- Automatic Documentation: Digital recording of auscultatory findings.
The combination of portable technology and artificial intelligence is democratizing access to specialized diagnoses.
3ds Max Modeling Guide
To recreate this innovative device in 3ds Max, start by meticulously organizing the project. Open the software and save the file as smart_stethoscope.max, setting the units to the metric system to maintain realistic proportions. Create layers for each component: Tubes, Earpieces, Head, Screen, Sensors. This organization will be crucial for an efficient workflow. 💡
Main Body Modeling
Create the flexible tube using a Spline with Sweep modifier to achieve natural and organic curvatures. For the stethoscope head, start with a Cylinder and apply Boolean operations to create the internal cavity that captures sounds. The earpieces and silicone tips can be modeled using modified spheres and capsules, paying attention to the characteristic ergonomics of these medical devices.
Incorporation of Technological Elements
The rectangular screen is a distinctive element of this smart stethoscope. Model a thin box and apply Bevel to smooth the edges, creating the feel of a modern touchscreen. Add small buttons and sensors using scaled-down cylinders and boxes, integrating these components in a way that makes them appear functional and cohesive with the overall design.
Realistic Materials and Textures
Assign specific materials to each component: the tubes require a black rubber material with low gloss and visible roughness, while the head needs polished metal with soft reflections. The screen should simulate glass with an opacity map and faint emission to indicate it is on. These material details are essential to convey the realism of the device.
Lighting and Final Render
Set up professional studio lighting using main area lights and secondary lights to highlight metallic reflections and the screen. An environmental HDRI will provide soft and realistic global lighting. For the render, use V-Ray or Arnold with global illumination and specular reflections enabled. In post-production, adjust the contrast to highlight the materials and add a subtle glow to the screen.
With a stethoscope that analyzes heartbeats better than a cardiologist after three cups of coffee, patients might soon ask: "Was that a murmur or is the battery running out?" Technology advances, but medical humor stays the same. 😅