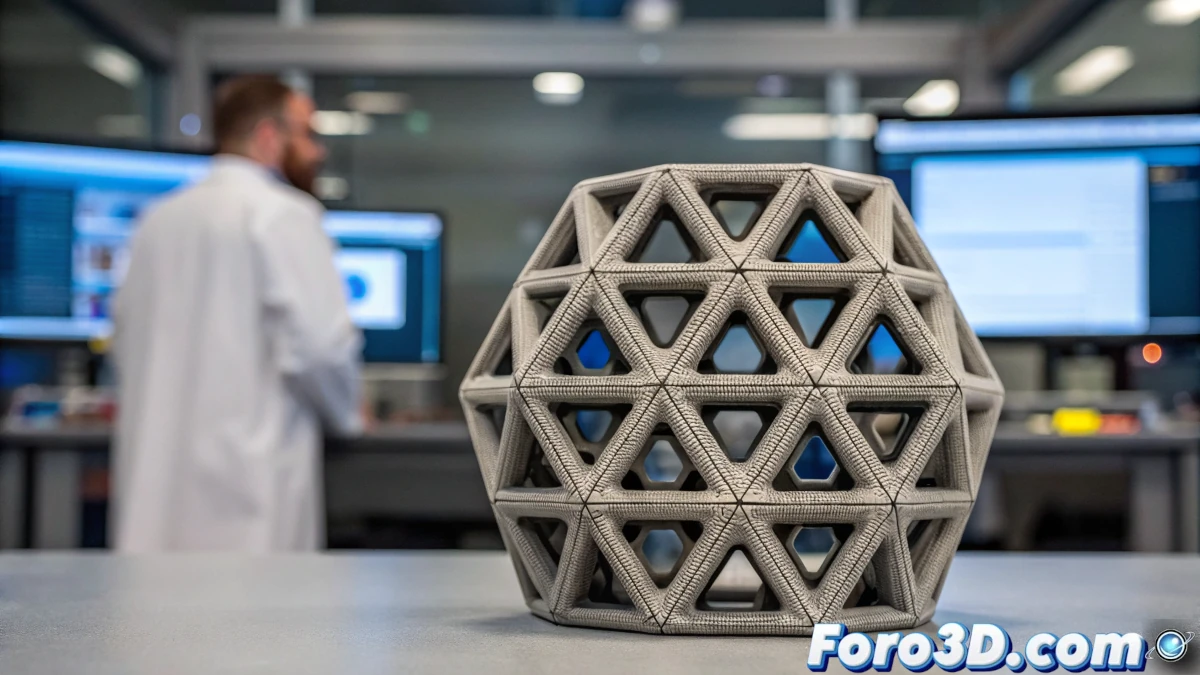
Innovations in Material Structure
3D printing has enabled the manufacturing of components with unprecedented precision, but the strength of the materials remains a key challenge. Researchers have found a way to improve durability by introducing irregular patterns into the material's structure.
Designs Inspired by Nature
In nature, structures like bone and mother-of-pearl have evolved to be highly resistant thanks to small irregularities in their composition. Applying this principle, researchers have developed a method that redistributes the connection points within printed materials, improving their resistance to fractures.
“The key to improving strength is not in reinforcing the material, but in how its structure is organized.”
Testing and Validation of the Method
To verify the effectiveness of this design, computational simulations and physical tests were performed on various polymers used in 3D printing. The results showed that these materials can withstand impacts more effectively and have a lower tendency to form cracks.
- Greater Strength: the enhanced materials withstand up to 2.6 times more tension before fracturing.
- Maintained Stiffness: structural stability is not compromised.
- Universal Application: compatible with various additive manufacturing techniques.
Impact on Industry
This technique does not require additional materials or chemical treatments, making it viable for sectors such as aerospace, automotive, and biomedical. The possibility of manufacturing stronger components without increasing production costs represents a significant advance in additive manufacturing.
The Future of 3D Printed Materials
The optimization of structural design in 3D printing demonstrates that small changes can generate great benefits. With this innovation, additive manufacturing moves towards more efficient and reliable production, enabling the development of more durable parts for various applications.