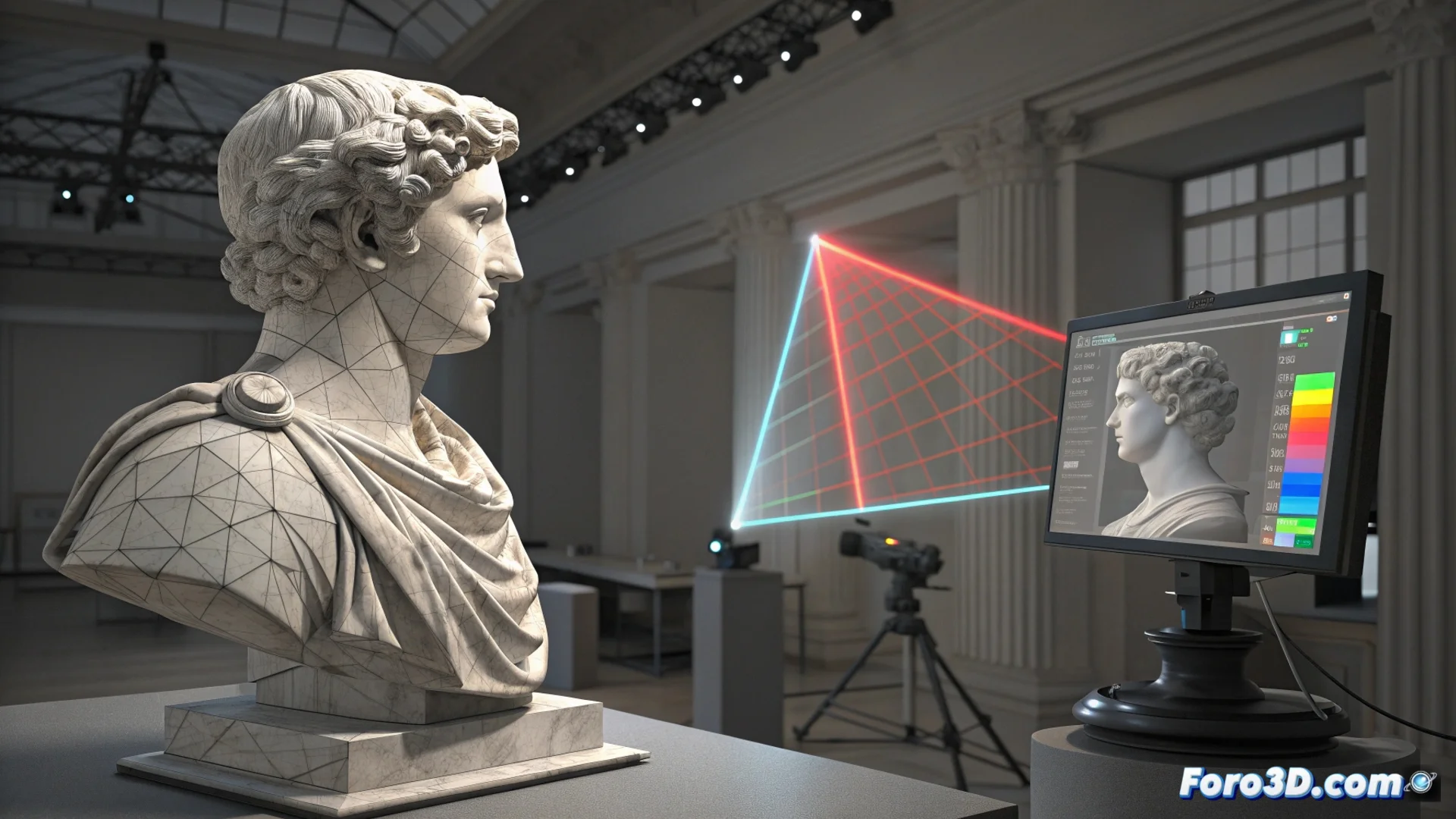
3D Comparison Detects Alterations in Sculptures
Three-dimensional digitization technology offers a digital magnifying glass to examine sculptural works with extreme precision. By comparing these digital models with historical files, researchers can discover hidden modifications. This method brings to light interventions such as repairs or additions that were never recorded, allowing to track the material history of the piece and confirm its authenticity. 🔍
The Workflow for Comparing 3D Models
The procedure begins by digitizing the current sculpture using a high-resolution 3D scanner. Subsequently, this model is registered and aligned with a previous scan or, if available, with the original design of the creator. Specialized software processes the two point clouds to calculate the geometric deviations between them. The system produces intuitive color maps that visualize where the shape varies, clearly marking the areas that have been modified.
Key Steps in the Analysis Process:- Digitize the piece with high-fidelity scanning equipment.
- Align the current 3D model with historical reference data.
- Process the point clouds to measure millimeter deviations.
A restored finger may point in a very different direction from the one the artist conceived, revealing more than some would like to show.
Interpreting the Findings from Comparative Scanning
The discrepancies identified by the technology require expert evaluation. A variation in surface texture may suggest a restoration where different materials were used. A change in volume may indicate that a lost section was reconstructed. Conservators combine this data with laboratory analysis and historical records to determine the nature and timing of the intervention.
Types of Alterations That Can Be Identified:- Surface variations due to the use of different restoration materials.
- Volume changes from reconstructing damaged or missing parts.
- Unrecorded interventions that affect the original geometry.
The Impact on Heritage Conservation
This methodology not only verifies authenticity but also documents the material life of the work. It provides an objective basis for deciding on future conservations and helps write a more accurate history of the art. Technology thus acts as an impartial witness to time. 🗿